توضیحات
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
Epidemiology
-
300,000 cases / ear in US (#1 after skin cancer), 41,000 deaths / year (#2 after lung cancer)
-
20% of American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetimes; 3% die of prostate cancer
-
Age adjusted incidence is increasing
-
99% with clinical disease are age 50+
-
A sizable minority of prostate cancers, those with Gleason score 3+3=6 (or less), have been shown almost never to metastasize to lymph nodes and lately it has been proposed to designate these not even as cancer, but by the name Indolent Lesion of Epithelial Origin (IDLE)
-
However, most pathologists endorse that Gleason 3+3=6 cancer is still cancer and a variety of surgical and non-surgical management options are now available for low-grade cancer
-
Low grade or "latent" cancers comprise 20% in cancers in men in their 50's, and 70% in men in 70's; usually one must examine the entire gland to find them
-
Clinical disease and high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) are more common in African-Americans than whites; blacks have higher stage at presentation, but stage adjusted survival is similar
-
Clinical disease is rare in Asians (3 - 4 / 100,000 vs 50 - 60 / 100,000 in US whites); higher rates in Scandinavians; all groups have similar incidence of latent cancers, suggesting importance of environmental or other genetic factors
-
No carcinoma if prepubertal castration, low incidence with hyperestrogenism (liver cirrhosis)
-
Not associated with sexually transmitted disease, smoking, occupational exposure, diet, nodular hyperplasia
Sites
-
Prostatic apex is more often involved than the bladder base
-
Peripheral zone is more often involved than transition zone or central zone
-
Posterior peripheral zones are more often involved than anterior / lateral horns of the peripheral zones
-
But bladder base, transitional / central zone and anterior / lateral horns of peripheral zones are more difficult to sample
Clinical features
-
Prostate cancer is detected by digital rectal exam (DRE), transurethral ultrasound (misses 30% of carcinomas that are isoechoic), or elevated PSA (either above 4 ng/dL or increasing over time)
-
Some evidence favors using > 2.5 ng/dL as a cutoff for biopsies to miss fewer cancers, particularly in men over 6
Microscopic (histologic) description
-
Gleason grade 1
-
Gleason score of 1+1=2 is extremely rare
-
Most cases that were diagnosed as Gleason score 1+1=2 in the era of Gleason would today be referred to as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH; adenosis)
-
Originally described as single, separate, closely packed, uniform round glands arranged in a circumscribed nodule with pushing borders
-
Separation of glands at the periphery from the main collection by more than one gland diameter indicates a component of at least grade 2
-
Should not be diagnosed on needle biopsy
-
Gleason grade 2
-
Like grade 1 but more variability in gland shape and more stroma separating glands, such that glands are separated by less than one gland's width
-
Less circumscribed at periphery, although no infiltration into stroma or between benign glands
-
Tends to be in transition zone (periurethral)
-
While it may be acceptable to diagnose Gleason 2 on prostatectomy or transurethral resection, it should not be diagnosed on needle biopsy since:
-
Grade 2 cancer is uncommon in the peripheral zone
-
Grade 2 is subject to marked inter-pathologist variability
-
Grade 2, assigned by non-urologic pathologists, usually reflects undergrading compared with experts
-
Grade 2 cancer in needle biopsy tissue does not predict better findings than grade 3 at radical prostatectomy
-
Gleason grade 3
-
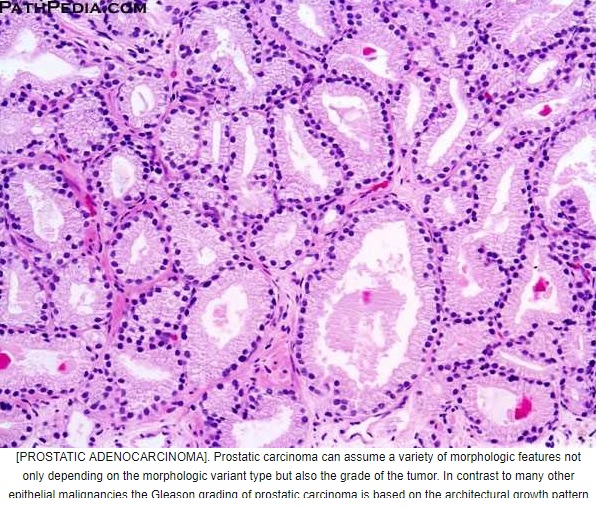
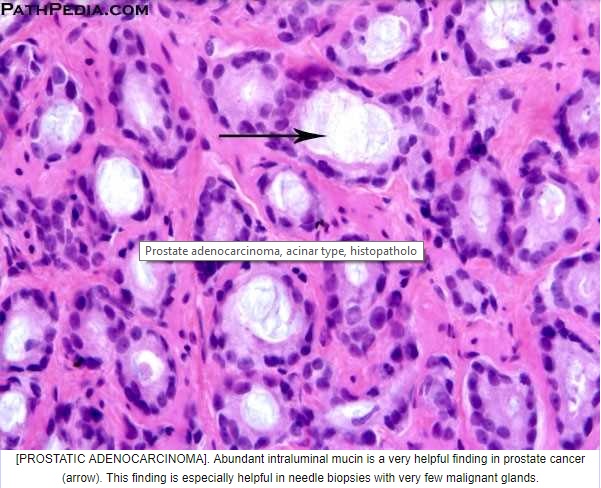
Single, separate, much more variable glands, may be closely packed but usually irregularly separated, ragged, poorly defined edge, but still in circumscribed structure, looser than a nodule, slightly infiltrative, still has intervening stroma between neighboring glands
-
Tangentially cut glands may appear as if they are poorly formed but should not get graded as a 4 unless poorly formed and fused glands persist on several levels
-
Patterns of Gleason grade 3 prostatic adenocarcinoma:
-
(a) Most common pattern is well formed, relatively uniform glands infiltrating between benign glands; glands may be angulated or compressed, separated by > 1 gland diameter
-
(b) Small glands with pinpoint lumina, glands still separate
-
(c) Medium sized glands with undulating luminal contours or large glands with a pseudoatrophic appearance
-
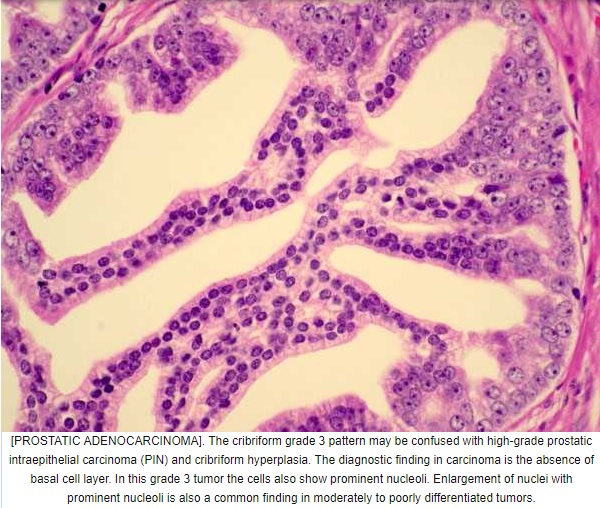
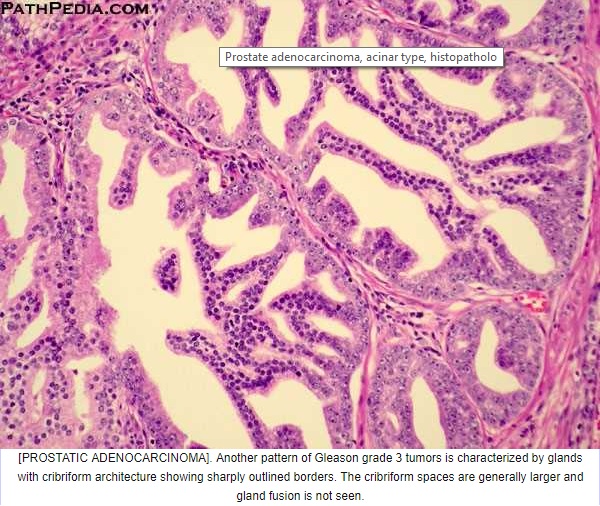
Cribriform cancer no longer qualifies as Gleason 3, even if the glands are similar in size to normal glands
-
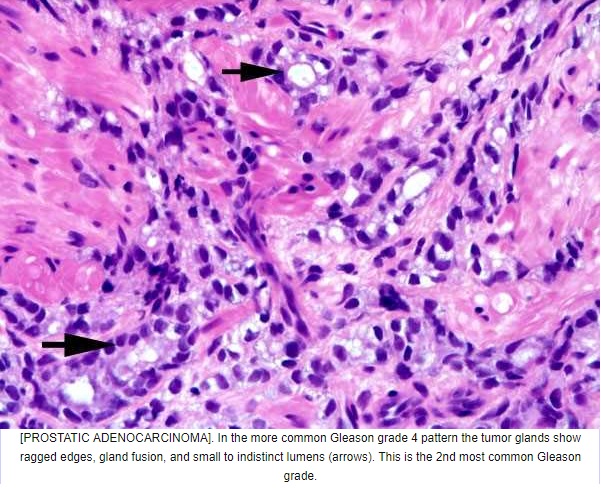
Gleason grade 4
-
Coalescent or fused glands
-
Absence of intervening stroma between adjacent glands constitutes fusion
-
Patterns of Gleason grade 4 prostatic adenocarcinoma:
-
(a) Most common is small acinar structures, some with well formed lumina, fusing into cords or chains; may be undergraded as Gleason 3
-
(b) Papillary or cribriform tumors with irregular / invasive edges; includes many but not all endometrioid carcinomas; nodule of cribriform gland should be larger than normal prostate gland; large nodules of cribriform Gleason 4 lack supporting stroma and tend to fragment; thus large fragments of cribriform glands on needle biopsy represents Gleason 4
-
Contemporary research supports grading all cribriform cancer as Gleason 4 because the presence and amount of cribriform cancer carries a distinctly adverse prognosis for recurrence) and for death from cancer
-
Note: basal cell markers are crucial in distinguishing cribriform high grade PIN, cribriform intraductal carcinoma (IDC) and invasive cribriform carcinoma
-
Note: patients with Gleason 8 at biopsy may have Gleason 7 at prostatectomy due to unsampled Gleason 3
-
(c) Hypernephroid pattern, with nests of clear cells resembling renal cell carcinoma; small, hyperchromatic nuclei; fusion of acini into more solid sheets with the appearance of back to back glands without intervening stroma
-
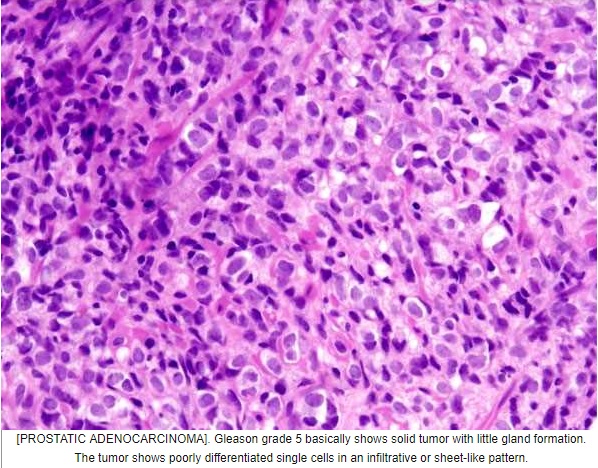
Gleason grade 5
-
Grade 5: two patterns
-
Comedonecrosis: central necrosis with intraluminal necrotic cells or karyorrhexis within papillary / cribriform spaces
-
single cells, possibly forming cords, possibly with vacuoles (signet ring cells) but without glandular lumens
-
This pattern may mimic lymphocytes at low power
-
Gleason 5 pattern has moderately good reproducibility, although certain patterns are more problematic
-
Gleason 5 cancer is often missed or underdiagnosed on needle biopsy
-
The presence of Gleason grade 5 in prostate biopsy specimens predicts higher rates of metastasis and death compared to Gleason 4+4=8 cancer
.jpg)